Summary
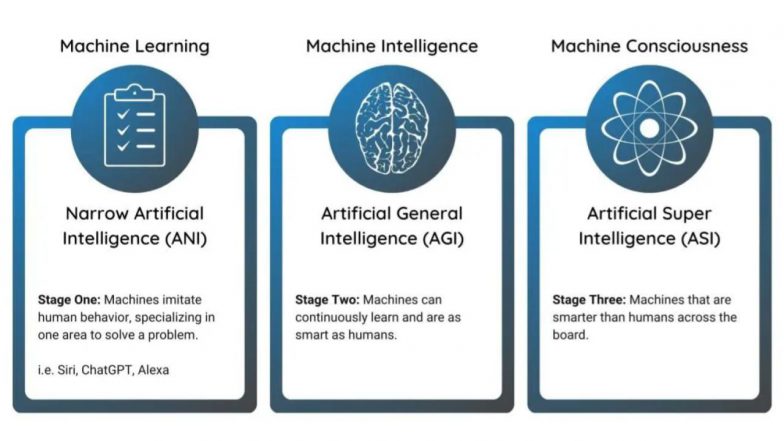
Narrow AI can be classified as being “limited to a single, narrowly defined task. Most modern AI systems would be classified in this category.” Artificial general intelligence is conversely the opposite.
- Definition:
ANI is AI designed to perform a specific task or solve a narrowly defined problem.
- Examples:
Virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa, facial recognition systems, recommendation engines, and chatbots.
- Limitations:
ANI lacks general cognitive abilities and cannot learn beyond its programmed capabilities.
- Current Status:
ANI is the type of AI that exists and is widely used today.
OnAir Post: Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI)
About
Applications and risks
Some examples of narrow AI are AlphaGo, self-driving cars, robot systems used in the medical field, and diagnostic doctors. Narrow AI systems are sometimes dangerous if unreliable. And the behavior that it follows can become inconsistent. It could be difficult for the AI to grasp complex patterns and get to a solution that works reliably in various environments. This “brittleness” can cause it to fail in unpredictable ways.
Narrow AI failures can sometimes have significant consequences. It could for example cause disruptions in the electric grid, damage nuclear power plants, cause global economic problems, and misdirect autonomous vehicles. Medicines could be incorrectly sorted and distributed. Also, medical diagnoses can ultimately have serious and sometimes deadly consequences if the AI is faulty or biased.
Simple AI programs have already worked their way into our society unnoticed. Autocorrection for typing, speech recognition for speech-to-text programs, and vast expansions in the data science fields are examples. As much as narrow and relatively general AI is slowly starting to help out societies, they are also starting to hurt them as well. AI had already unfairly put people in jail, discriminated against women in the workplace for hiring, taught some problematic ideas to millions, and even killed people with automatic cars.[10] AI might be a powerful tool that can be used for improving lives, but it could also be a dangerous technology with the potential for misuse.
Despite being “narrow” AI, recommender systems are efficient at predicting user reactions based their posts, patterns, or trends. For instance, TikTok’s “For You” algorithm can determine user’s interests or preferences in less than an hour. Some other social media AI systems are used to detect bots that may be involved in biased propaganda or other potentially malicious activities.
Source: Wikipedia
Web Links
ANI vs. AGI
A Deep Dive on the Differences Between Narrow AI and AGI
Source: SingularityNet
Narrow AI — Specialized and Task-Specific
Narrow AI, also known as Weak AI, is designed to perform a specific task or a narrow range of tasks. It operates within predefined parameters and lacks the capability to perform tasks outside its designated domain.
Examples of Narrow AI include voice assistants like Siri and Alexa, which can set reminders, play music, and provide weather updates. Recommendation systems used by platforms like Netflix and Amazon suggest movies, TV shows, and products based on user preferences. Image and speech recognition technologies identify objects in images or transcribe spoken words into text, while autonomous vehicles rely on AI to navigate roads and make driving decisions. Even OpenAI’s ChatGPT is a form of Narrow AI — although it excels at understanding and generating human-like text based on the input it receives, it does not possess general intelligence, consciousness, or self-awareness.
Narrow AI excels at specific tasks due to its ability to process large amounts of data and identify patterns. However, it lacks the versatility and general problem-solving abilities of human intelligence or an artificial general intelligence. It cannot transfer knowledge from one domain to another or understand the broader context of its actions… the way an AGI would.